Announcements
Jensen Huang’s “ChatGPT Moment for Robotics” — and Superb AI as a Key Partner for Physical AI

Hyun Kim
Co-Founder & CEO | 2026/01/13 | 5 min read
At CES 2025, NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang said AI now understands the laws of physics and that “The next frontier of AI is physical AI. The ChatGPT moment for general robotics is right around the corner.” In this year’s keynote, he declared that the moment is “nearly here.”
- “The ChatGPT moment for robotics is here. Breakthroughs in physical AI — models that understand the real world, reason, and plan actions — are unlocking entirely new applications. NVIDIA’s full stack of Jetson robotics processors, CUDA, Omniverse, and open physical AI models empowers our global ecosystem of partners to transform industries with AI-driven robotics.” - Jensen Huang
This suggests that AI models have crossed a threshold—moving beyond digital data to understand and interact with the physical world. In 2026, robots are expected to move beyond the lab and into everyday settings such as factories, homes, and roads—making physical AI something we encounter up close.
So far, the Superb AI blog has covered NVIDIA’s physical AI strategy and expansion. Today, we’ll break down how physical AI emerged as a core theme at CES 2026—and what NVIDIA’s strategy looks like this year.
1. The Brain and Heart of Physical AI: NVIDIA and the Race for Next-Generation Chipsets
To make physical AI a reality, advanced computing power is essential.
At CES 2026, NVIDIA unveiled its next-generation AI chip, Vera Rubin, opening up new possibilities. With inference performance improved by 5 times and training performance by 3.5 times compared with Blackwell, the chipset provides a powerful brain for robots that must compute complex physical laws in real time. AMD also intensified the competition by unveiling its Helios platform, claiming a 10x increase in compute performance.
But what matters even more than hardware is the rise of robot foundation models. NVIDIA unveiled a broad open-model ecosystem for physical AI.
- NVIDIA Cosmos: A world model for physics-based synthetic data generation and simulation. It helps robots learn the laws of physics in a virtual world before they are deployed in the real world.
- GR00T N1.6: A Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model specialized for humanoid robots, enabling them to understand human language and control the whole body to perform tasks.
This marks a shift—from an era when robot developers had to code every motion from scratch to one where they fine-tune large models to give robots “intelligence.”
2. Robots Move Beyond the Lab — Into Everyday Life and Real-World Sites
Advances in physical AI have quickly translated into breakthroughs in robot hardware. Notably, Korean companies stood out with strong momentum.
- Hyundai Motor Group’s Next-Generation Atlas Model: Rebuilt from hydraulic to fully electric, Atlas demonstrated motions that surpass human physical limits—rotating its joints 360 degrees. Hyundai said it plans to deploy the robot in real factories starting in 2028, signaling that physical AI is moving beyond a “demo spectacle” and becoming a true production tool.
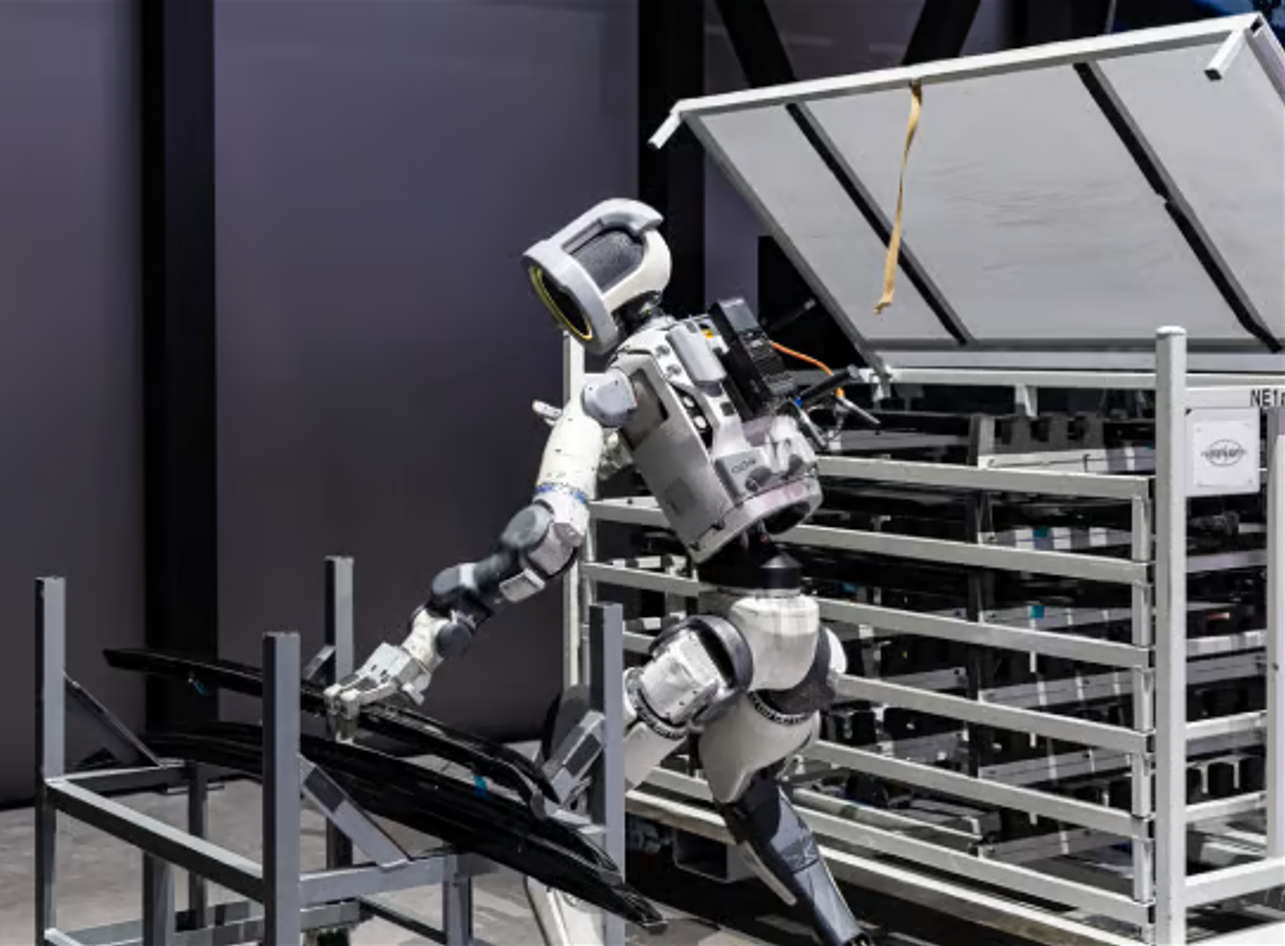

Atlas. Source: Hyundai Motor Group
- LG Electronics’ Cloyd: LG’s home-assistant robot, Cloyd, demonstrated delicate household tasks such as moving laundry, organizing towels, and placing bread into an oven.
- HL Mando: HL Mando showcased the commercialization potential of domain-specific physical AI through a robot that can identify and repair divots on golf courses.
Beyond Korea, global companies such as Boston Dynamics and Neura Robotics unveiled humanoids powered by NVIDIA’s Jetson Thor—demonstrating that robots are evolving into autonomous machines that can make decisions and move on their own.
3. The Real Challenge Is Closing the Sim-to-Real Gap
Despite the optimistic vision showcased at CES 2026, major barriers to commercializing physical AI remain—namely, the data gap and the Sim-to-Real mismatch (mismatch between simulation and the real world).
Unlike generative AI, which can learn from online text and images, physical AI requires data from a 3D physical world filled with unpredictable variables—gravity, friction, lighting changes, and more. Training robots by making them fall tens of thousands of times in the real world is nearly impossible in terms of cost and time.
That’s why, at CES, “synthetic data” and “simulation”—both emphasized by Jensen Huang—emerged as core solutions. Frameworks such as NVIDIA’s Isaac Lab-Arena and OSMO focus on training robots at scale in virtual environments and streamlining the process of transferring that intelligence into the real world.
4. The Physical AI Ecosystem and Partnerships
Physical AI is a massive industry that no single company can dominate. It requires the convergence of diverse technologies—from hardware and AI models to simulation, data processing, and communications. To foster this ecosystem, NVIDIA runs its startup program, NVIDIA Inception.
At CES 2026, Les Karpas, global head of physical AI at NVIDIA Inception, introduced key partners expected to lead the physical AI era. He drives collaboration between NVIDIA and robotics and physical AI startups worldwide—serving as a bridge to help these teams build smarter robots, safer factories, and higher-performance machines in the real world.
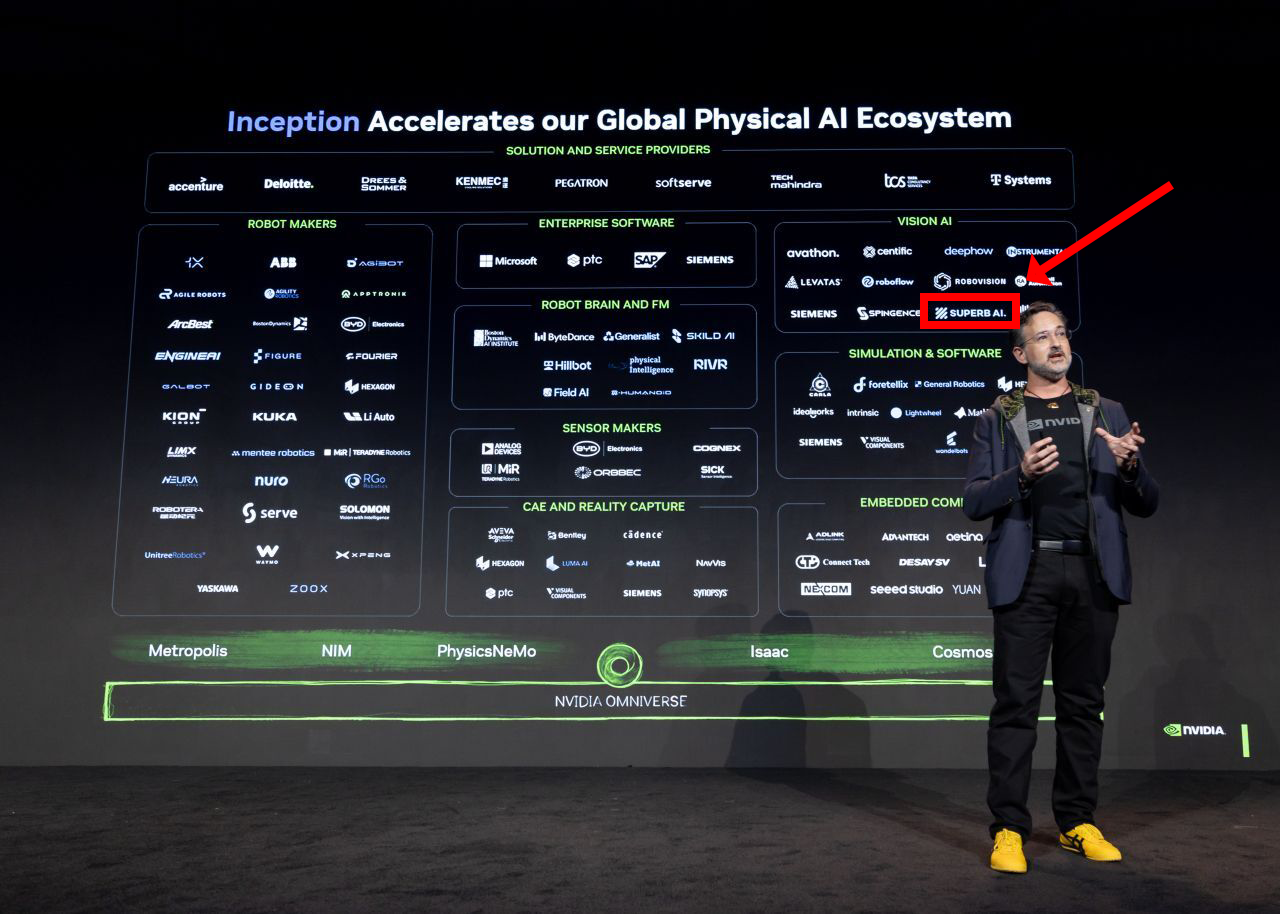
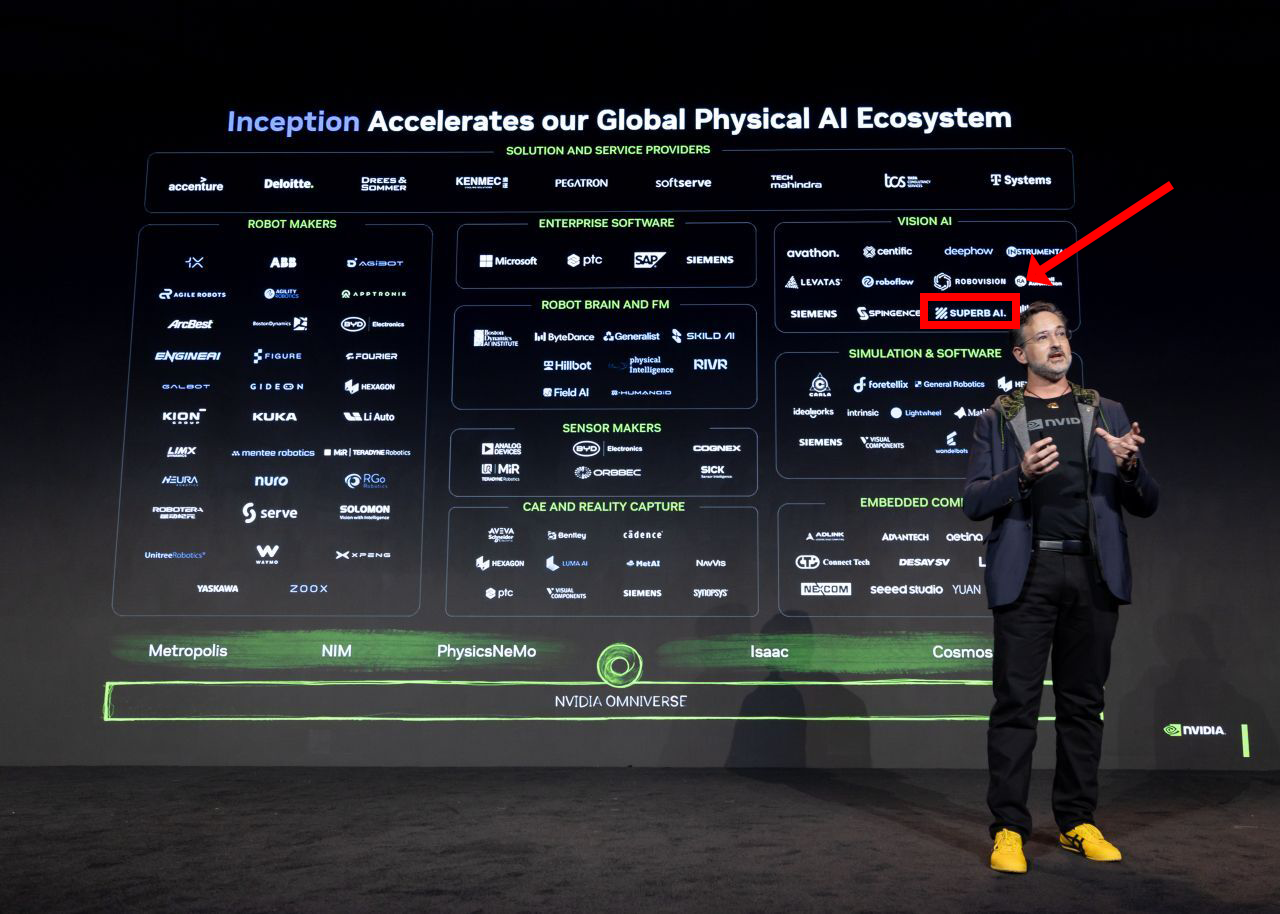
NVIDIA lists Superb AI as a key partner in Vision AI, Source: NVIDIA for Startups
If you look at the slide, you’ll see Superb AI listed as a Vision AI partner—and it is the only Korean company among the Vision AI partners.
Vision AI serves as a robot’s “eyes” and “judgment.” Physical AI must continuously interpret incoming visual data, and in particular, convert unexpected situations (edge cases) into data so the model can be retrained on an ongoing basis. The real world is infinitely complex, and it’s impossible to preprogram every situation a robot may encounter. Robots must keep learning through data collected in the field.
Superb AI provides a data-centric AI platform designed to solve this challenge. We offer the infrastructure to curate, label, and manage high-quality data so that models deployed on robots can be optimized for each industrial site—whether in factories, retail, construction, and more.
Superb AI also has real-world deployments using NVIDIA’s VSS, including applications at Incheon International Airport and CS WIND.
CES 2026 signaled that AI is moving beyond the stage of “thinking” and into the stage of “acting.” As Jensen Huang declared, physical AI is no longer a research project—it is becoming a major industrial shift.
In line with this shift, Superb AI is focused on advancing the “eyes” of physical AI through Vision AI technology and data curation capabilities, thereby closing the Sim-to-Real gap.
In 2026, Superb AI will continue to serve as a key partner to global companies like NVIDIA—delivering standout Vision AI solutions and establishing itself as a core player in the global physical AI market.
As the era of physical AI approaches, if you’re looking for practical AI solutions that go beyond technological progress and can be applied directly on-site, leave your contact information below. Superb AI experts will reach out shortly.
Related Posts

Announcements
Superb AI Joins NVIDIA’s Physical AI Ecosystem as a Key Vision AI Partner

Hyun Kim
Co-Founder & CEO | 20 min read

Announcements
Superb AI Named to AIIA’s “2026 Emerging AI+X Top 100” List

Hyun Kim
Co-Founder & CEO | 2 min read

Announcements
Superb AI Raises About $10 Million in Pre-IPO Funding Ahead of Planned 2026 IPO

Hyun Kim
Co-Founder & CEO | 10 min read

About Superb AI
Superb AI is an enterprise-level training data platform that is reinventing the way ML teams manage and deliver training data within organizations. Launched in 2018, the Superb AI Suite provides a unique blend of automation, collaboration and plug-and-play modularity, helping teams drastically reduce the time it takes to prepare high quality training datasets. If you want to experience the transformation, sign up for free today.
