Announcements
Superb AI Wins Hanwha Systems AI Challenge for Second Year in a Row for Infrared Video Analysis Technology

Hyun Kim
Co-Founder & CEO | 2025/05/22 | 10 min read

Superb AI Wins Hanwha Systems AI Challenge for Second Year in a Row with Infrared Video Analysis Technology
Superb AI has claimed the top spot at the Hanwha Systems AI Challenge for the second year in a row. Following Researcher Eunsoo Lim’s victory in 2024, the team of Seunghyeon Kim and Kyeongryeol Go brought home another first-place finish in 2025.
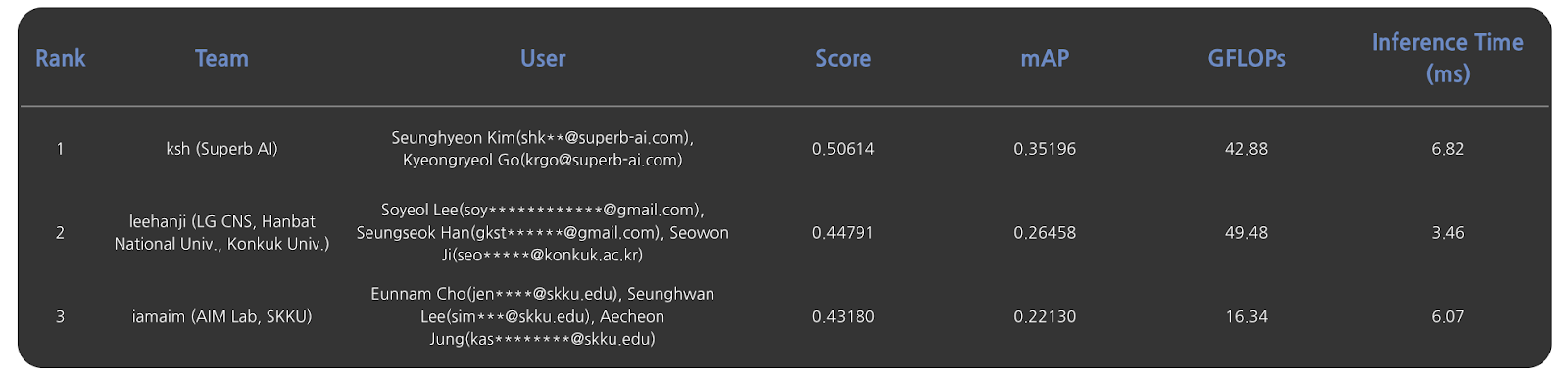
Hanwha AI Challenge Leaderboard
(Final Results of the Hanwha Systems AI Challenge 2025)
The competition challenges participants to develop AI models capable of accurately detecting objects in infrared camera footage—comprehensively evaluating not only accuracy but also inference speed, a critical factor in real-world industrial applications. It serves as a proving ground for infrared video processing technologies used in advanced fields such as defense, autonomous driving, and security.
The team’s research was also presented at the Thermal Infrared in Robotics 2025 workshop at the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2025, earning global recognition for Superb AI’s technological capabilities.
The Technical Challenges of Infrared Video Analysis
What makes infrared (IR) video analysis so difficult? Unlike standard RGB images, infrared data presents a unique set of challenges that make it especially hard to work with:
Data Scarcity
High-quality infrared image datasets are extremely limited and often come with strict licensing restrictions.
- Need for Specialized Equipment: Capturing infrared images requires thermographic cameras—not regular optical ones. These devices are expensive, often costing thousands of dollars, and require expert handling.
- Limited Industrial Usage: Infrared imaging is mainly used in specialized fields such as defense, industrial inspection, medical diagnostics, and perimeter security. As a result, public access to IR data is far more restricted compared to widely available RGB imagery.
- Environmental Sensitivity: Infrared data is highly sensitive to external conditions such as weather, ambient temperature, and the thermal properties of the objects being captured. This makes it technically challenging to obtain data with consistent quality.
- Lack of Open-Source Datasets: Unlike large RGB datasets like ImageNet or COCO, open-source IR datasets are few and far between. They tend to be small in scale and limited to specific scenarios—such as building heat loss or specific road condition analyses.
Security and Regulatory Barriers
IR footage captured in military or security settings is often classified, making it difficult or even impossible to share or publish.
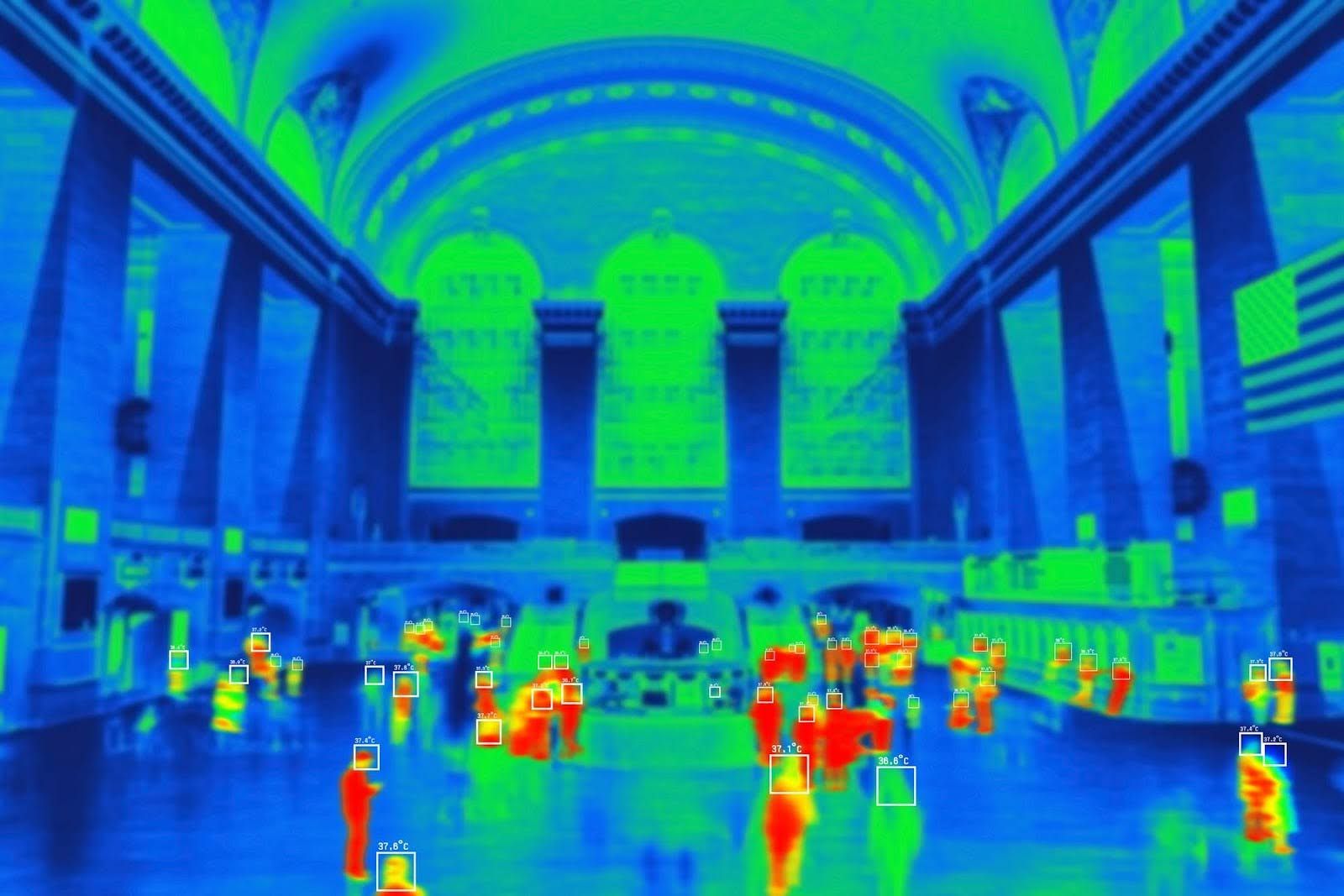

Class Imbalance
On top of the data scarcity issue, class imbalance is another major hurdle in infrared video analysis. It’s already a challenging problem even for RGB data with abundant samples—but in the case of IR data, where data is inherently scarce, the problem becomes even more serious and “collecting more data” is not a realistic solution.
- Common Imbalance Patterns: Common object classes like “person” or “car” are relatively well represented, while data for rarer objects such as “truck,” “bicycle,” or “special-purpose vehicle” is significantly lacking.
- Stronger Biases in IR Data: The imbalance is even more severe in infrared datasets. For example, in this year’s challenge dataset, there were 26,932 instances of “car” and 13,495 of “person”—but only 55 samples of “special-purpose vehicles.”
- Multiple Barriers to Data Collection: To collect additional samples for these underrepresented classes, one would need to ① design scenarios that include the target objects, ② capture them using thermal imaging equipment, and ③ accurately label the data—all of which introduce major logistical and technical hurdles.
- Risk of Model Bias: Without addressing this imbalance, AI models tend to overfit to dominant classes and struggle to recognize rare ones—leading to recognition failures that can pose serious risks, especially in high-stakes domains like defense and security.
Domain-Specific Challenges
Infrared data differs fundamentally from RGB images, making it difficult to apply conventional computer vision models trained on RGB datasets.
- Different Representation of Information: RGB cameras capture light reflections to render color and texture, whereas infrared cameras detect heat emissions to visualize temperature distributions—resulting in entirely different representations of visual characteristics for the same scene.
- Limits of Transfer Learning: Models pre-trained on large-scale RGB datasets like ImageNet (e.g., ResNet, EfficientNet) often show significant performance degradation when applied directly to IR imagery. This is because visual features such as color, texture, and edges are represented very differently in infrared images compared to RGB images.
- Difference in Feature Extraction: Techniques like edge detection or texture analysis, which work well for RGB images, often underperform in infrared images. In IR data, for example, object outlines are determined by temperature contrast, which can vary over time.
- Environmental Variability: Infrared images are highly sensitive to ambient temperature, weather, and time of day—making it far more complicated to build models that perform consistently across different conditions.
- Difficulty in Data Standardization: While RGB imaging benefits from standardized color spaces and processing methods, IR imaging varies significantly depending on the equipment and measurement method used—complicating the overall pre-processing steps.
These challenges are well known in sectors like defense and security, where data is often obtained in sensitive or highly controlled environments. The restricted availability of such data remains one of the most significant obstacles to building effective AI models in these fields.
Superb AI’s Innovative Approach
One of the most common reasons AI projects fail in enterprise settings is the lack of sufficient, high-quality data. This challenge is even more pronounced in sectors like defense, security, and other specialized industries where data access is severely restricted. To address this fundamental issue, Superb AI developed a practical yet innovative approach.
1. A Scientific Approach to Model Selection
The 2025 challenge revealed the following key evaluation criteria used to assess submissions:
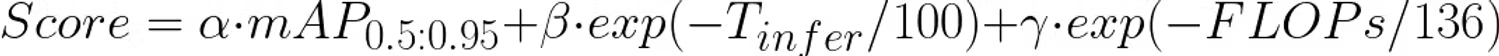
Accuracy (Mask AP), real-time performance, and computational efficiency (FLOPs) were all considered important evaluation criteria, as a model that is highly accurate but computationally heavy can be impractical in real-world applications. The goal was to strike a balance—delivering high performance while remaining lightweight enough for fast inference.
Many companies tend to adopt the latest trending models without much scrutiny, often leading to excessive costs and wasted resources. In contrast, Superb AI developed an innovative, data-driven model selection process focused on maximizing business ROI by carefully evaluating both accuracy and efficiency—instead of simply opting for the most well-known models.
While other participants focused solely on familiar architectures like YOLO or DETR, the Superb AI team performed a comparative analysis of various RTMDet-Ins model variants to determine the optimal choice. Specifically, the team trained both RTMDet-Ins-x, which supports real-time instance segmentation, and Co-DETR-Ins, which offers outstanding mask accuracy (Mask AP) but slower processing speed.
Ultimately, RTMDet-Ins-x yielded the highest overall score. The RTMDet-Ins model family includes multiple versions—such as -x, -l, -m, -s, and -tiny—but training every variant from scratch within the limited challenge timeframe was not feasible. Instead, the team referenced official benchmark results of the models on the COCO dataset and used them to analyze which model would deliver the most balanced performance across the competition’s composite metrics: accuracy, inference speed, and computational efficiency.
Through this data-informed decision-making process, the team concluded that RTMDet-Ins-s offered the best trade-off, achieving 0.387 Mask AP, 1.93 ms inference time, and 43.0 G-FLOPs for the number of calculations. In particular, its indirect measure for comparison—0.5399—was the highest among all variants, suggesting it would deliver the most robust performance in real-world operating environments.
Model Evaluation and Selection Process
2. Data Augmentation Using Generative AI
AI performance is ultimately determined not by model complexity, but by the quality and diversity of the data it learns from.
While most participating teams focused on optimizing their models—through techniques like model compression, ensembling, or TensorRT conversion—Superb AI took a different path by tackling the root problem: insufficient data. The belief that data quality and diversity matter more than architecture itself guided the team’s entire strategy. This differentiated, data-first approach was a key factor behind Superb AI’s consecutive wins.
Traditionally, securing a high-quality dataset could require months of data collection and significant financial investment. To overcome this, Superb AI leveraged cutting-edge generative AI technology to fundamentally solve the data scarcity issue. The team adopted two innovative methods:
Maximizing the Use of Existing Data (RGB → IR Conversion)
The first method involved converting existing RGB images into IR images. Instead of capturing new datasets using expensive thermal cameras, Superb AI repurposed standard RGB images already in hand. By converting images from a wide range of environments and conditions into IR format, the team was able to significantly enhance model robustness.

RGB → IR conversion process
For example, if deploying an IR video analysis AI to a nighttime surveillance system in a restricted military area where real IR footage is unavailable, Superb AI’s Superb Platform can transform daytime RGB footage into IR data—rapidly securing training data without compromising access restrictions.
Generating Custom IR Images from Text Prompts
The second method involved creating entirely new IR images using text prompts. This approach goes beyond simple RGB-to-IR conversion—enabling the generation of novel IR images that reflect completely new situations and scenarios.
The team used descriptive text prompts to generate new IR images tailored to the training scenarios and automatically labeled them to create training data.
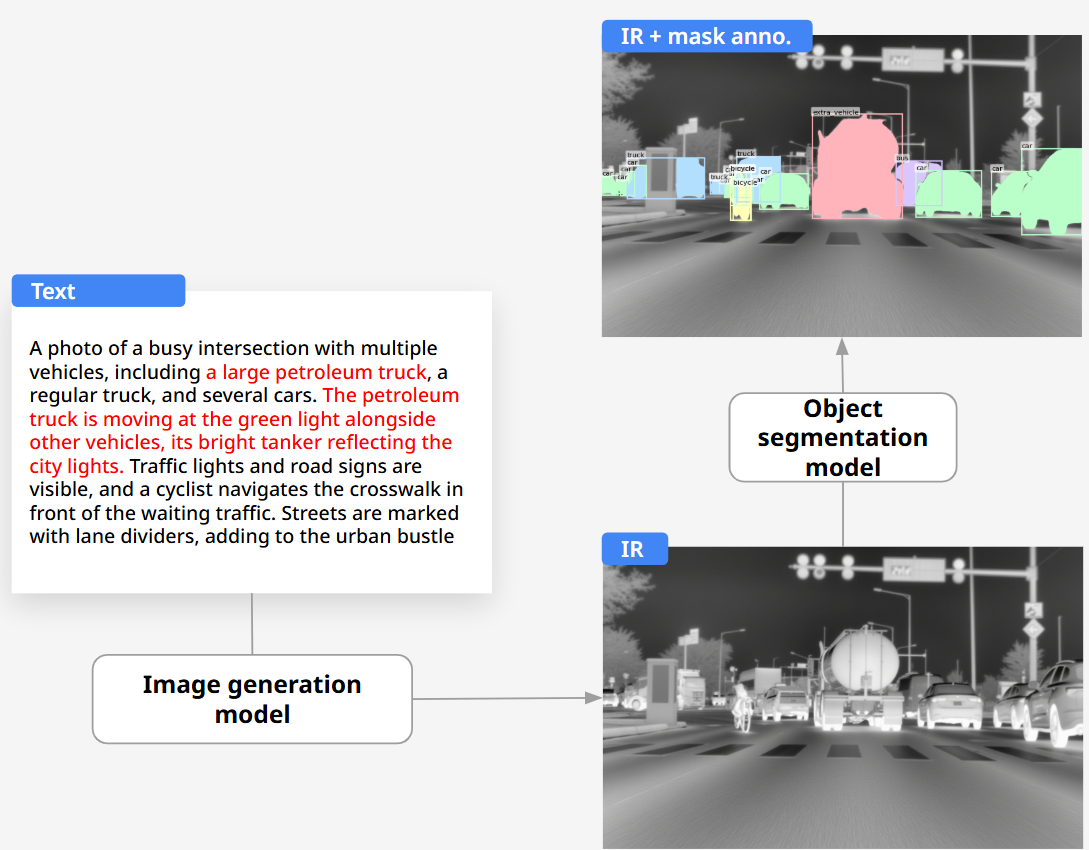
Generating new IR images using text prompts
By using text prompts alone, this method enables the generation of diverse data across a wide range of scenarios—while also making it easy to synthesize rare edge cases that may occur in real-world environments. Furthermore, it strengthens data security by allowing training data to be created in-house without exposing sensitive information externally.
Superb AI’s team was able to generate rare IR scenes—such as “a nighttime road with an oil tanker waiting at a traffic light”—in just a few hours, a process that would otherwise require months of planning and on-site shooting.
Using this approach, the team selectively augmented underrepresented classes in the Audi Autonomous Driving Dataset (A2D2), extracting 2,136 images featuring rare objects such as bicycles, trucks, tractors, and utility vehicles from the original 41,277-image dataset to address class imbalance.
3. Smarter Learning Strategies: Achieving Maximum Performance with Minimal Data
Superb AI’s research team employed a pseudo-labeling strategy, allowing the model to serve as its own teacher by assigning labels to unlabeled data. Starting with a small set of verified samples, the team was able to automatically label a large volume of previously unlabeled data—dramatically reducing the time and cost required for manual annotation while achieving even higher performance.
The training pipeline followed a progressive learning strategy, which included supervised pretraining, semi-supervised pretraining, and fine-tuning. During the fine-tuning phase, the team enhanced recognition performance by increasing data variety—adjusting infrared image brightness, modifying object sizes, and synthesizing them into diverse scenes. As a result, they improved the model’s Mask AP from 0.320 to 0.362—an approximate 13% performance gain over the baseline.
Real-World Impact: From Defense to Autonomous Driving
This advancement goes far beyond just winning a competition. It demonstrates a scalable approach to solving real-world problems across multiple industries:
Defense & Security
- Enhanced accuracy for night-time surveillance and monitoring systems
- High-performance AI models built even in data-scarce environments
- Improved thermal-based object detection and tracking systems
Autonomous Driving & ADAS
- Better recognition in poor weather and low-light conditions
- Improved accuracy in multi-sensor fusion systems
- Lightweight models capable of real-time inference
Smart City & Surveillance
- Thermal-based anomaly detection systems
- Robust object recognition across varied environmental conditions
- Energy-efficient, 24/7 monitoring solutions
Superb AI’s Innovative Winning Formula
This achievement in the AI Challenge was made possible by the synergy of Superb AI’s two core strengths:
1. A Data-Centric Approach to AI Development
Instead of focusing solely on model optimization, the team prioritized data quality and diversity. This data-centric AI philosophy is central to Superb AI’s strategy and serves as a key competitive advantage—especially in industries where data is difficult to obtain.
2. A Complete MLOps Pipeline
Superb AI provides a full MLOps pipeline that supports the entire AI development lifecycle—from dataset creation to model deployment. This end-to-end solution is optimized for data-constrained industries such as manufacturing, autonomous systems, physical security, and monitoring.
Facing Data Challenges in Specialized AI Applications?
If you're struggling with these problems:
- AI projects are delayed due to limited training data
- Model performance drops in harsh or uncommon conditions (e.g., nighttime, bad weather)
- AI implementation costs exceed expectations
- Manual labeling demands excessive time and human resources
Superb AI is built to solve exactly these problems. Winning the Hanwha Systems AI Challenge two years in a row isn’t just a technical feat—it’s proof of our ability to tackle real-world industrial challenges head-on.
Related Posts

Announcements
Superb AI Raises About $10 Million in Pre-IPO Funding Ahead of Planned 2026 IPO

Hyun Kim
Co-Founder & CEO | 10 min read

Announcements
Superb AI Secures Patents in Korea, U.S., and Japan for AI Data Selection and Lightweight Fine-Tuning Technologies, Strengthening Global Competitiveness

Hyun Kim
Co-Founder & CEO | 15 min read

Announcements
Introducing ZERO: Korea’s First Vision Foundation Model Tailored for Industry

Hyun Kim
Co-Founder & CEO | 10 min read

About Superb AI
Superb AI is an enterprise-level training data platform that is reinventing the way ML teams manage and deliver training data within organizations. Launched in 2018, the Superb AI Suite provides a unique blend of automation, collaboration and plug-and-play modularity, helping teams drastically reduce the time it takes to prepare high quality training datasets. If you want to experience the transformation, sign up for free today.
